Blockchain Technology
📑 5 slides
👁 45 views
📅 1/19/2026
Introduction to Blockchain
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger recording transactions across many computers.

2
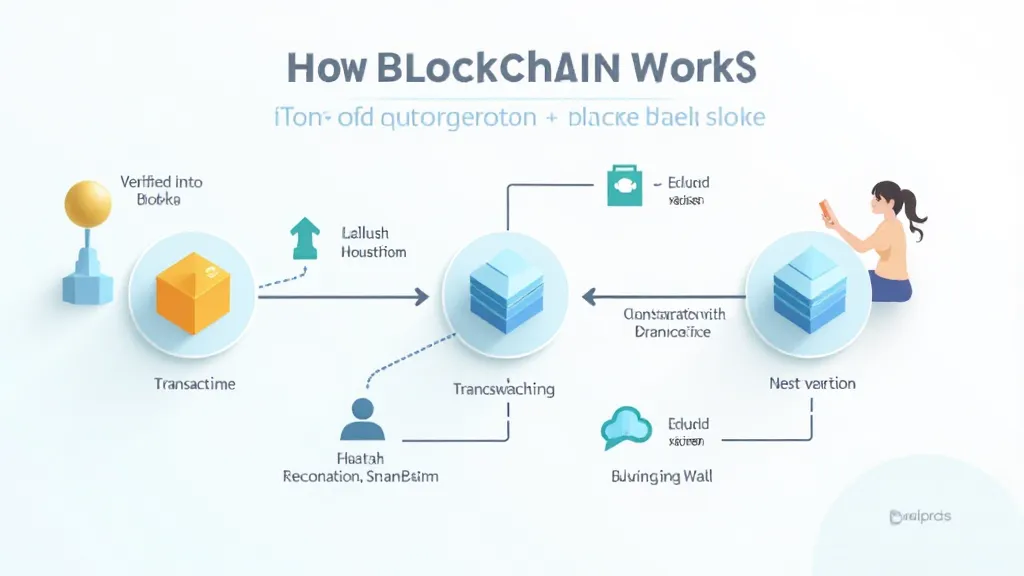
How Blockchain Works
- Transactions are grouped into blocks and verified by network nodes through consensus algorithms.
- Once verified, blocks are added to the chain in a linear, chronological order, ensuring immutability.
- Public blockchains are transparent, while private blockchains restrict access to authorized participants.
3
Applications of Blockchain
- Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum use blockchain for secure, peer-to-peer transactions.
- Smart contracts automate agreements without intermediaries, used in finance and supply chains.
- Blockchain enhances data security in healthcare, voting systems, and intellectual property management.

4
Benefits & Challenges
- Benefits: Decentralization reduces fraud, increases transparency, and lowers transaction costs.
- Challenges: Scalability issues, high energy consumption (e.g., Bitcoin mining), and regulatory uncertainty.
- Future solutions include layer-2 scaling (e.g., Lightning Network) and eco-friendly consensus mechanisms.

5
Conclusion & Future Outlook
- Blockchain is transforming industries by enabling trustless, secure, and efficient systems.
- Adoption is growing in finance, logistics, and governance, with potential for Web3 and metaverse integration.
- Ongoing innovations aim to address current limitations, making blockchain a cornerstone of future technology.

1 / 5